GDP Q2 2020 Preliminary Estimate
- GDP fell by 20.4% in Q2 2020 compared to the previous quarter, following the 2.2% fall in the first quarter – the largest quarterly contraction since records began in 1955.
- As a result of the two consecutive quarters of decline, the UK fell into recession for the first time since 2009.
- Compared with the same quarter a year ago, the UK economy fell by 21.7%.
- The record fall in the second quarter was driven by a sharp decline in April. As restrictions were lifted, and the economy reopened, output improved, with monthly data for June suggesting that GDP increased 8.7% on the month.
- Services, production and construction output all fell at a record rates in Q2 2020, down 19.9%, 16.9% and 35.0% respectively.
UK, Quarter 1 (Jan to Mar) 2020 and Quarter 2 (Apr to June) 2020
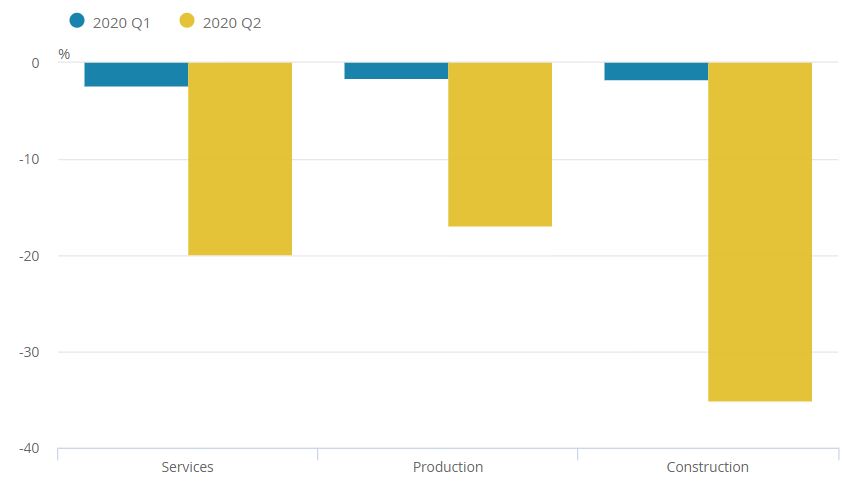
Source: ONS
Services
Services output fell by 19.9% in Q2 2020 on the previous quarter – a record fall, driven by declines across most industries.
Indeed, declines were most severe in the accommodation and food services (86.7%), wholesale and retail trade (-20.0%), human health and social work activities (-27.2%), and education (-34.4%) sectors which accounted for over half (52.4%) of the contraction in services output in Q2.
The monthly data suggests that growth picked up in the latter stages of the quarter, Indeed, services output grew by 7.7% in June, following growth of 1.5% in May and a fall of 18.5% in April. The wholesale, retail and repair of motor vehicles sub-sector was the largest contributor, driven by a recovery in the motor vehicles industry.
Despite the rise in June, services output remains 17.6% lower than pre-pandemic levels.
Production
Production output fell by 16.9% in Q2 2020, driven by a 20.4% monthly decline in production output in April. All four sub-sectors reported a decline.
Manufacturing output fell by 20.2% in Q2 2020, driven by decreases in the manufacture of transport equipment (-49.1%) as factories shutdown during the period. Just 381,357 cars were produced in the first six months of the year (source: SMMT) - the worst performance over six months since 1954.
Monthly data suggests that production output grew by 9.3% in June, with manufacturing growing by 11.0%. That said, production output is 11.6% lower than pre-covid-19 levels, with manufacturing 14.2% lower.
Construction
Construction output fell by 35.0% in Q2 compared with the previous quarter driven by declines in new work and repair and maintenance.
New orders fell by 51.1% in Q2, as both all other work (-51.9%) and new housing (-49.0%) recorded sharp declines.
The recent Bank of England Summary of Business Conditions report suggested that a weakness in private sector demand is resulting in “significantly lower” construction output compared with a year ago.
Monthly data suggests that construction output grew by 23.5% in June following growth of 7.6% in May and a record fall of 40.2% in April 2020. New housing and private new housing (18.1% weight to construction) were the main drivers, the latter rising by 42.3% following sharp declines in March and April.
That said, construction output remains 24.8% lower than pre-covid-19 levels.
Household consumption
Household consumption fell by 23.1% in Q2 2020, the largest contraction on record. The decline was driven by falls in spending on net tourism, restaurants and hotels, and transport.
The fall in private consumption accounted for over 70% of the fall in GDP in the second quarter.
Back to Retail Economic News